Object Store Configuration
In Kubeflow Pipelines (KFP), there are two components that utilize Object store:
- KFP API Server
- KFP Launcher (aka KFP executor)
The default object store that is shipped as part of the Kubeflow Platform is SeaweedFS. However, you can configure a different object store provider with your KFP deployment.
The following diagram provides an simplified overview of how object storage is utilized and configured:
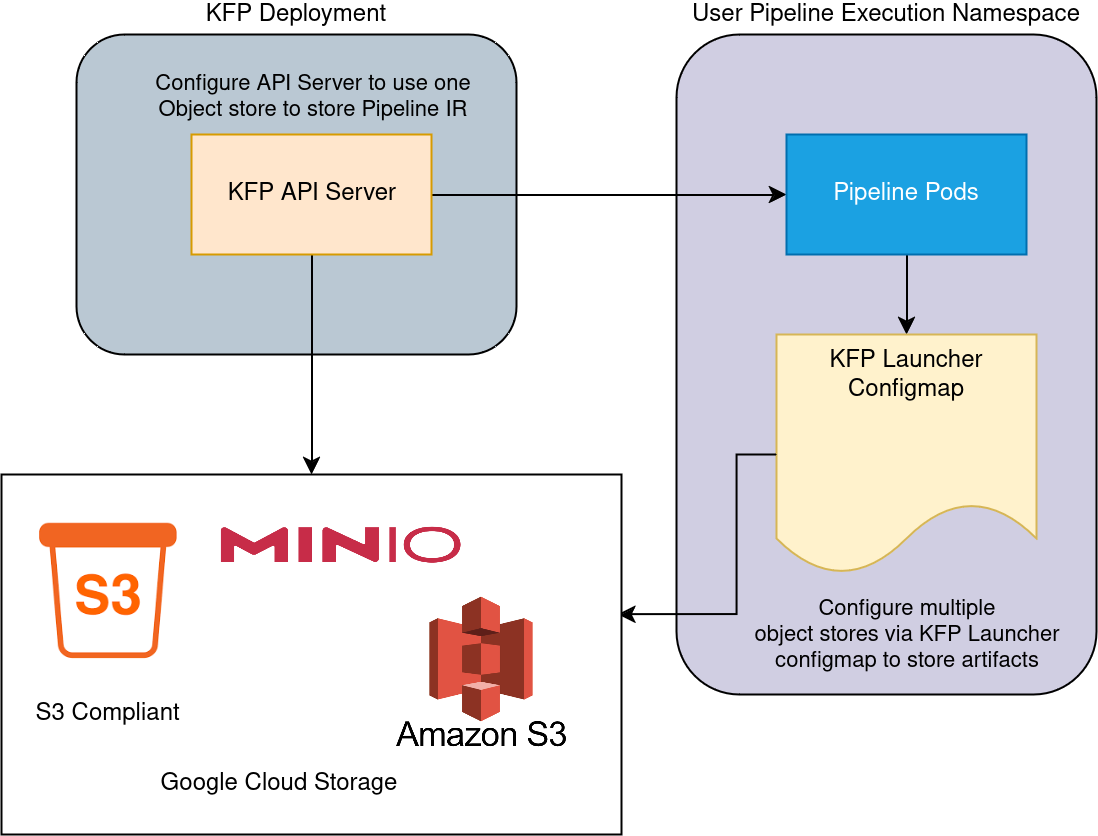
Prerequisites
- Admin level access to KFP Kubernetes namespace
- Object Store credentials for a supported provider (see below)
Note: in this doc “KFP Namespace” refers to the namespace where KFP is deployed. If KFP is deployed as part of the Kubeflow Platform deployment, this is the
kubeflownamespace.
KFP API Server
The KFP API Server uses the object store to store the Pipeline Intermediate Representation (IR).
The list below describe the type of Object Store configurations supported today for API Server. Static credentials here refers to long term credentials provided by Object Store providers.
For AWS Static Credentials and other S3 compliant object storage, this consists of an Access Key ID and Secret Access Key ID embedded into the run time environment or, passed as secure parameters to some API. In Google Cloud Storage, this refers to a JSON containing the GCS APP Credentials.
API Server Supported providers
| Provider | Supported |
|---|---|
| SeaweedFS with Static Credentials | Yes |
| SeaweedFS Gateway to AWS/GCP/Azure/Minio S3 | Yes |
| AWS S3 with Static Credentials | Yes |
| AWS S3 with IRSA | Yes |
| S3-Compliant Storage with Static Credentials | Yes |
| Google Cloud Storage with Static Credentials | No |
| Google Cloud Storage with App Credentials | No |
API Server Object Store Configuration
To configure the object store used by the KFP API Server, the configuration depends on whether you are using static credentials, or AWS S3 with IAM roles for service accounts (IRSA).
Static credentials
To configure an AWS S3 bucket with static credentials you will need to add the following environment variables to your KFP API Server deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ml-pipeline
namespace: kubeflow
spec:
...
template:
...
spec:
containers:
- name: ml-pipeline-api-server
serviceAccountName: "ml-pipeline"
env:
...
- name: OBJECTSTORECONFIG_HOST
value: "your-bucket" # e.g. s3.amazonaws.com
- name: OBJECTSTORECONFIG_PORT
value: "port" # e.g. 443
- name: OBJECTSTORECONFIG_REGION
value: "region" # e.g. us-east-1
# true if object store is on a secure connection
- name: OBJECTSTORECONFIG_SECURE
value: "true"
# These env vars reference the values from a Kubernetes secret
# this requires deploying the secret ahead of time, and filling out the
# following values accordingly.
- name: OBJECTSTORECONFIG_ACCESSKEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: "some-key-1"
name: "secret-name"
- name: OBJECTSTORECONFIG_SECRETACCESSKEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: "some-key-2"
name: "secret-name"
AWS IRSA (IAM Roles for Service Accounts)
To utilize AWS IRSA for KFP API Server, you will need to omit any Static credential configuration from your deployment, namely OBJECTSTORECONFIG_ACCESSKEY and OBJECTSTORECONFIG_SECRETACCESSKEY , as these take precedence. If they are left in, API Server will ignore any IRSA configuration.
Next, ensure the appropriate IAM roles associated with the Kubernetes Service Account ml-pipeline in the KFP namespace. This is highly dependent on your platform provider, for example for EKS see the IRSA docs.
KFP Launcher
The KFP launcher uses the object store to store KFP Input and Output Artifacts.
The list below describe the type of Object Store configurations supported today for API Server.
Refer to the API Server configuration section here for more information on what Static Credentials are.
KFP Launcher Supported providers
| Provider | Supported |
|---|---|
| SeaweedFS with Static Credentials | Yes |
| SeaweedFS Gateway to AWS/GCP/Azure/Minio S3 | Yes |
| AWS S3 with Static Credentials | Yes |
| AWS S3 with IRSA | Yes |
| S3-Compliant Storage with Static Credentials | Yes |
| Google Cloud Storage with Static Credentials | Yes |
| Google Cloud Storage with App Credentials | Yes |
KFP Launcher Object Store Configuration
To configure the object store utilized by the KFP Launcher, you will need to edit the kfp-launcher Kubernetes ConfigMap.
In a default KFP deployment, this typically looks like:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kfp-launcher
namespace: user-namespace
data:
defaultPipelineRoot: ""
Note: If this configmap is not provided, you will need to deploy this in the Kubernetes Namespace where the Pipelines will be executed. This is not necessarily the same namespace as where Kubeflow Pipeline itself is deployed.
The defaultPipelineRoot is a path within the Object store bucket where Artifact Input/Outputs in a given pipeline are
stored. Note that this field can also be configured via the KFP SDK, see SDK PipelineRoot Docs. It can also be configured via the
KFP UI when creating a Run.
By default defaultPipelineRoot is minio://mlpipeline/v2/artifacts and artifacts are stored in the default SeaweedFS deployment.
The first value in the path mlpipeline refers to the bucket name.
If you want artifacts to be stored in a different path in the bucket that is not /v2/artifacts, you can simply change the defaultPipelineRoot.
For example to store artifacts in /some/other/path within the default SeaweedFS install, use the following KFP Launcher configmap:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kfp-launcher
namespace: user-namespace
data:
defaultPipelineRoot: "minio://mlpipeline/some/other/path"
Note: that when utilizing the KFP Launcher configmap it needs to be deployed in the same namespace where the Pipelines will be created. In a standalone KFP deployment this is the KFP namespace. In a Kubeflow Platform deployment, this will be the user Kubeflow Profile namespace.
Configure other Providers
To utilize a different object store provider entirely, you will need to add a new field providers to the KFP launcher configmap.
How to configure this field depends on your object store provider. See below for details.
Note that the provider is determined by the PipelineRoot value. If PipelineRoot=s3://mlpipeline then this is matched
with the s3 provider. If PipelineRoot=gs://mlpipeline then this is matched with the gs provider (GCS) and so on.
S3 and S3-compatible Provider
To configure an AWS S3 bucket with static credentials, update your KFP Launcher configmap to the following:
apiVersion: v1
data:
defaultPipelineRoot: s3://mlpipeline
providers: |-
s3:
default:
endpoint: s3.amazonaws.com
disableSSL: false
region: us-east-2
forcePathStyle: true
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: your-k8s-secret
accessKeyKey: some-key-1
secretKeyKey: some-key-2
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kfp-launcher
namespace: user-namespace
The s3 provider field is valid for any s3 compliant storage. The default indicates that this configuration is used
by default if no matching overrides are provided (read about overrides).
S3 IRSA and Environment based Credentials
If you are using AWS IRSA, or you have embedded your bucket credentials in the task environment (e.g. via SDK Secret Env),
then you can set fromEnv: true and omit secretRef. This would look something like:
apiVersion: v1
data:
defaultPipelineRoot: s3://mlpipeline
providers: |-
s3:
default:
endpoint: s3.amazonaws.com
disableSSL: false
region: us-east-2
forcePathStyle: true
credentials:
fromEnv: true
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kfp-launcher
namespace: user-namespace
Ensure that the service account being used to run your pipeline is configured with IRSA (see IRSA docs).
You can also configure static credentials via AWS Environment variables directly in your pipeline, for example:
kubernetes.use_secret_as_env(
your_task,
secret_name='aws-s3-creds',
secret_key_to_env={'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY': 'AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY'})
kubernetes.use_secret_as_env(
your_task,
secret_name='aws-s3-creds',
secret_key_to_env={'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID': 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID'})
kubernetes.use_secret_as_env(
your_task,
secret_name='aws-s3-creds',
secret_key_to_env={'AWS_REGION': 'AWS_REGION'})
...
Google Cloud Storage (GCS) provider
To configure a GCS provider with static credentials you need to only provide the reference to the App Credentials file via a Kubernetes Secret:
apiVersion: v1
data:
defaultPipelineRoot: gs://mlpipeline
providers: |-
gs:
default:
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: your-k8s-secret
tokenKey: some-key-1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kfp-launcher
namespace: user-namespace
You can also configure static credentials via GCS Environment variables directly in your pipeline, for example:
# Specify the default APP Credential path
your_task.set_env_variable(name='GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS', value='/gcloud/credentials.json')
# Mount the GCS Credentials JSON
kubernetes.use_secret_as_volume(your_task, secret_name='gcs-secret', mount_path='/gcloud')
GCS Environment based Credentials
If you have embedded GCS credentials in your Pipeline Task environment (e.g. via SDK Secret Env), you can set
fromEnv: true and omit the secretRef:
apiVersion: v1
data:
defaultPipelineRoot: gs://mlpipeline
providers: |-
gs:
default:
credentials:
fromEnv: true
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kfp-launcher
namespace: user-namespace
KFP Launcher Overrides
KFP Launcher overrides allow users to specify different Provider sources for different paths within a given PipelineRoot.
The following example shows a comprehensive example of how to do this for GCS and S3 compatible providers:
gs:
default:
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: gs-secret-1
tokenKey: gs-tokenKey
overrides:
# Matches pipeline root: gs://your-bucket/some/subfolder
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: some/subfolder
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: gcs-secret-2
tokenKey: gs-tokenKey-2
# Matches pipeline root: gs://your-bucket/some/othersubfolder
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: some/othersubfolder
credentials:
fromEnv: true
s3:
default:
endpoint: http://some-s3-compliant-store-endpoint.com
disableSSL: true
region: minio
forcePathStyle: true
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: your-secret
accessKeyKey: accesskey
secretKeyKey: secretkey
overrides:
# Matches pipeline root: s3://your-bucket/subfolder
# aws-s3-creds secret is used for static credentials
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: subfolder
endpoint: s3.amazonaws.com
region: us-east-2
forcePathStyle: false
disableSSL: false
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: aws-s3-creds
accessKeyKey: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
secretKeyKey: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# Matches pipeline root: s3://your-bucket/some/s3/path/a/b
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: some/s3/path/a/b
endpoint: s3.amazonaws.com
region: us-east-2
credentials:
fromEnv: true
# Matches pipeline root: s3://your-bucket/some/s3/path/a/c
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: some/s3/path/a/c
endpoint: s3.amazonaws.com
region: us-east-2
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: aws-s3-creds
accessKeyKey: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
secretKeyKey: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# Matches pipeline root: s3://your-bucket/some/s3/path/b/a
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: some/s3/path/b/a
endpoint: https://s3.amazonaws.com
region: us-east-2
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: aws-s3-creds
accessKeyKey: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
secretKeyKey: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
The keyPrefix are matched with the path prescribed in the PipelineRoot. For example if PipelineRoot is s3://your-bucket/some/s3/path/b/a Then the following provider config is used:
- bucketName: your-bucket
keyPrefix: some/s3/path/b/a
endpoint: https://s3.amazonaws.com
region: us-east-2
credentials:
fromEnv: false
secretRef:
secretName: aws-s3-creds
accessKeyKey: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
secretKeyKey: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
If a field is not provided, then the default configuration is utilized.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Thank you for your feedback!
We're sorry this page wasn't helpful. If you have a moment, please share your feedback so we can improve.